반응형
문제
간단한 그래픽 편집기를 콘솔 바탕으로 만들어보자. 그래픽 편집기의 기능은 "삽입", "삭제", "모두보기", "종료" 의 4가지이고, 실행 과정은 다음과 같다. (연결리스트 문제입니다.)
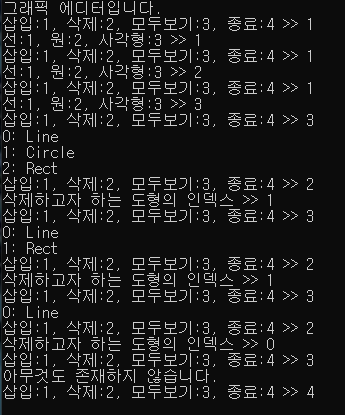
결과
소스코드
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape {
Shape* next;
protected:
virtual void draw() = 0;
public:
Shape() { next = NULL; }
void paint() { draw(); }
Shape* add(Shape* p) { this->next = p; return p; }
Shape* getNext() { return next; }
void setNext(Shape* p) { next = p; }
};
class Line : public Shape {
public:
virtual void draw() { cout << "Line" << endl; }
};
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
virtual void draw() { cout << "Circle" << endl; }
};
class Rect : public Shape {
public:
virtual void draw() { cout << "Rect" << endl; }
};
class UI {
public:
static int Mainmenu() {
int input;
cout << "삽입:1, 삭제:2, 모두보기:3, 종료:4 >> ";
cin >> input;
return input;
}
static int Insert() {
int input;
cout << "선:1, 원:2, 사각형:3 >> ";
cin >> input;
return input;
}
static int Delete() {
int input;
cout << "삭제하고자 하는 도형의 인덱스 >> ";
cin >> input;
return input;
}
};
class GraphicEditor {
Shape* pStart;
Shape* pLast;
int size;
public:
GraphicEditor() { pStart = NULL; pLast = NULL; size = 0; }
void make_shape() {
cout << "그래픽 에디터입니다." << endl;
while (true) {
int input;
input = UI::Mainmenu(); //처음 메뉴중 선택
switch (input)
{
case 1: //1번 선택시
input = UI::Insert(); // 도형 선택
newshape(input);
break;
case 2:
input = UI::Delete();
delshape(input);
break;
case 3:
show();
break;
case 4:
exit(1);
default:
cout << "존재 하지 않는 메뉴" << endl;
break;
}
}
}
void newshape(int input) {
switch (input)
{
case 1:
if (size == 0) { //처음 입력시
pStart = new Line();
pLast = pStart;
}
else //아닐 시
pLast = pLast->add(new Line());
size++;
break;
case 2:
if (size == 0) { //처음 입력시
pStart = new Circle();
pLast = pStart;
}
else //아닐 시
pLast = pLast->add(new Circle());
size++;
break;
case 3:
if (size == 0) { //처음 입력시
pStart = new Rect();
pLast = pStart;
}
else //아닐 시
pLast = pLast->add(new Rect());
size++;
break;
default:
cout << "존재 하지 않는 메뉴" << endl;
break;
}
}
void delshape(int n) {
Shape* removenode = NULL;
if (-1 > n || n > size - 1)
cout << "존재 하지 않습니다." << endl;
else {
if (n == 0)
{ //처음의 값을 삭제할 때는 pStart를 이용하여 삭제한다.
removenode = pStart;
pStart = pStart->getNext();
}
else { //아니라면
int i = 1;
for (Shape* p = pStart; p != NULL; p = p->getNext()) {
//pStart 다음 값부터 그 다음값이 NULL이 아닐때까지 반복
if (i == n) {
removenode = p->getNext();
//예) 1번째라면 이 반복문의 시작은 pStart이므로 다음 값을 삭제할 노드에 옮겨준뒤
p->setNext(removenode->getNext());
//p의 next가 가리키고 있는 노드를 현재의 p next로 옮겨주어 삭제할 노드를 한칸 띄어 이동하게 만든다.
}
i++;
}
}
size--;
delete removenode;
}
}
void show()
{
if (size == 0)
cout << "아무것도 존재하지 않습니다." << endl;
else {
int i = 0;
for (Shape* p = pStart; p != NULL; p = p->getNext()) {
cout << i << ": ";
p->paint();
i++;
}
}
}
};
int main() {
GraphicEditor* shape = new GraphicEditor;
shape->make_shape();
delete shape;
}
반응형
'명품C++프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 명품 C++ Programming 실습문제 10장 2번 (0) | 2021.06.06 |
|---|---|
| 명품 C++ Programming 실습문제 10장 1번 (0) | 2021.06.06 |
| 명품 C++ Programming 실습문제 9장 9번 (0) | 2021.06.06 |
| 명품 C++ Programming 실습문제 9장 7, 8번 (0) | 2021.06.01 |
| 명품 C++ Programming 실습문제 9장 6번 (0) | 2021.06.01 |

